CASCADE-ChemicAl Shift CAlculator using DEep learning
CASCADE stands for ChemicAl Shift CAlculation with DEep learning. It is a stereochemically-aware online calculator for NMR chemical shifts using a graph network approach developed at Colorado State University. Molecular input can be specified as SMILES or through the graphical interface. An automated workflow executes 3D structure embedding and MMFF conformer searching. The full ensemble of optimized conformations are passed to a trained graph neural network to predict the NMR chemical shift (in ppm) for each C atom.
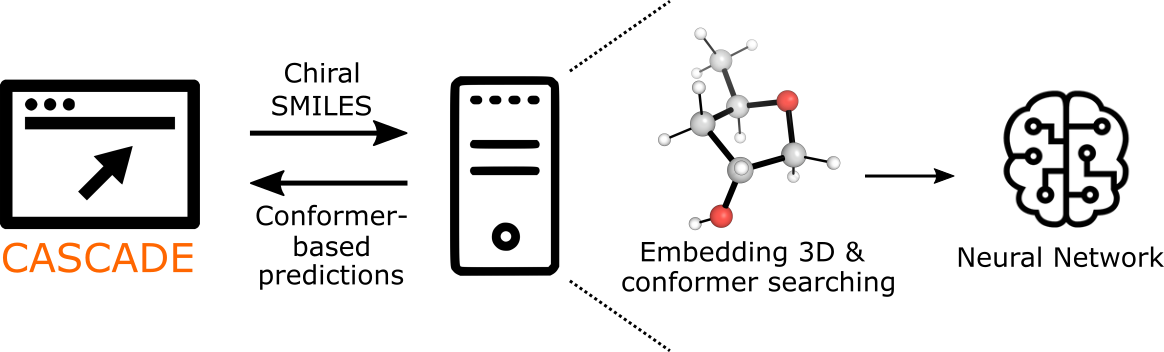
Graph Convolutional Neural Network
The graph Network considers each atom as a node in a molecular graph that permits communication between atoms - this is through edges connecting atom pairs. Each molecule is represented by a 3D molecular graph, in which each pair of atoms are connected by a distance (i.e., as opposed to solely representing bonds in a 2D molecular graph). The architecture of the network used is shown below.
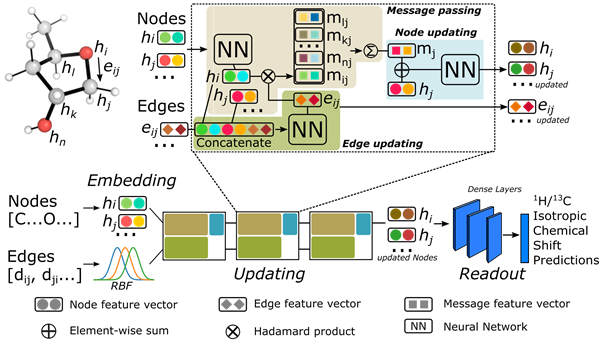
Performance evaluation
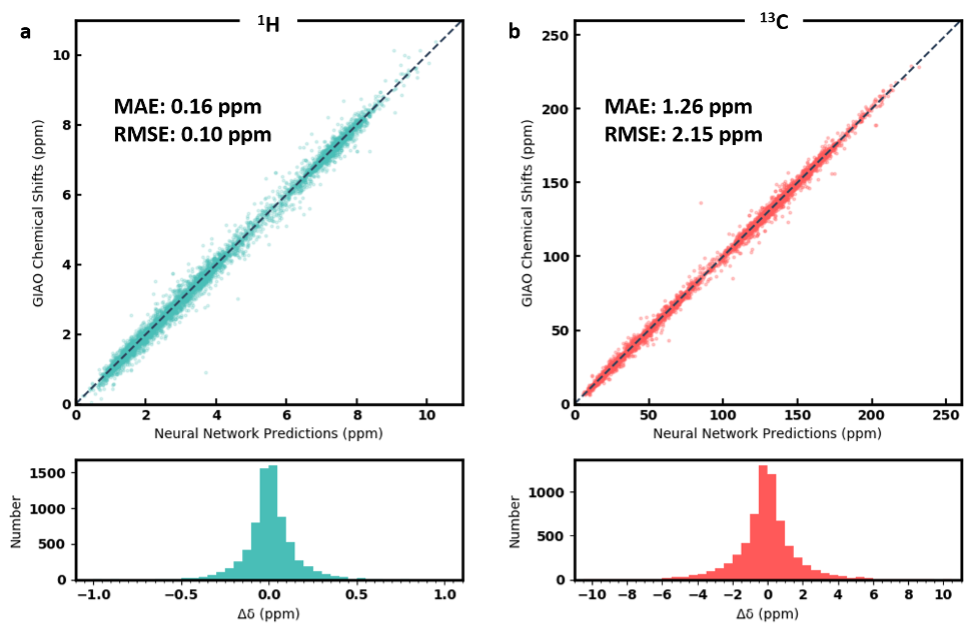
We evaluated the performance of three neural network models. The first model, DFTNN, takes DFT optimized structures as input and was trained against DFT calculated shielding tensors. The MAE for the 500 testing molecules is 1.26 ppm compared to mPW1PW91/6-311+G(d,p) DFT calculations. The second model, ExpNN-dft, which was trained against experimental chemical shifts using DFT optimized structures as input through transfer learning achieves a MAE of 1.25 ppm for the 500 testing molecules compared to experimental observed chemical shifts. The eventual model, Expnn-ff, which serves as the backend predictor for this web app takes MMFF optimized structures as input and predict experimental chemical shift. The performance of the eventual model on the testing molecules is 1.43 ppm compared to the experimental 13C chemical shifts. The Scatter plot and histogram show the correlation between predicted and experimental chemical shift are shown below.
Some Guidelines for using CASCADE:
- Remember to specify stereochemistry where appropriate
- Molecular composition is currently restricted to the following elements: C, H, N, O, S, P, F, Cl
- Molecules with formal charges are not processed.
- CASCADE generates conformers and performs energy minimizations with MMFF before predicting the chemical shifts. While there is no theoretical size-limit to this approach, extremely large molecules cause difficulties for webserver performance, particularly if multiple queries are submitted. For this reason we ask that you limit your molecules to 50 heavy atoms.
- For support with larger molecules, please install and run CASCADE on your own machine. The code is openly available: Gihub.
- For futher support please contact us by email: patonlab@colostate.edu
For more details, please see our paper:Real-time Prediction of 1H and 13C Chemical Shifts with DFT accuracy using a 3D Graph Neural Network. Guan, Y.; Sowndarya, S. S. V.; Gallegos, L. C.; St. John, P. C.; Paton, R. S. Chem. Sci. 2021, 23, 12012-12026. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1039/D1SC03343C.